Why Do They Check Your Elbows When Donating Plasma?
Many times, when donating plasma, the trained health personnel will check the inside of your elbow to draw blood. At times, he or she may draw blood at the back of your hands.
But before this happens, a finger prick test will be conducted to ascertain the quantity of hemoglobin or protein in your blood. This is known as the “hemoglobin test.” This test is important to find out whether you have enough red blood cells. If you do not have an adequate level of red blood cells, then you are anemic. This test is performed every time you intend to donate plasma.
During the period of the COVID-19 pandemic that led to the rising depletion of blood bank reserves in the US, the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) proposed an amendment to the existing guidelines. As a result of this, the deferral time has been shortened from 12 months to 3 months for the set of individuals:
- Males who have had sex with males (MSM)
- Females who have had sex with MSM
- Those who have had fresh piercings or tattoos
- Those who have traveled to regions where malaria is prevalent
Furthermore, people susceptible to Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) or who have someone in their family weren’t able to make a blood donation. But now, the FDA proposes this set of individuals who were ineligible can now reapply.
According to a former phlebotomist, another reason your elbow will be checked while donating plasma is for signs of intravenous (IV) drug use. Your elbows will be looked at for any sores, wounds, or rashes.
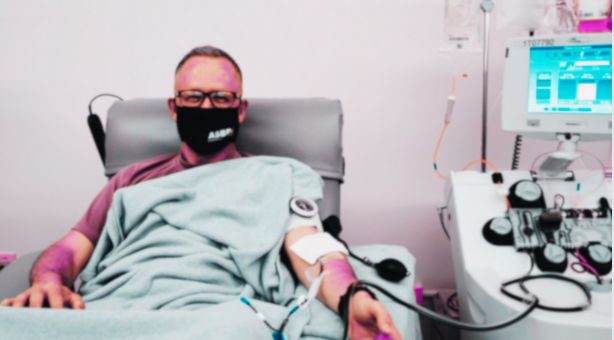
Plasma Donation
Plasma donation is simply the process of collecting blood to obtain plasma and transfer the rest of the blood to the blood via plasmapheresis, the separation of blood cells from the rest of plasma. It is important to note that plasma donation takes a bit longer than donating whole blood. However, the more you donate, the more quantity of blood plasma you generate.
People with AB blood type possess a universal plasma type, which implies that everyone can get this plasma without issue. This means patients in critical situations can get their plasma right away, which can save their lives.
If your blood type is AB, when you donate plasma, a particular component of your blood is utilized in the medical treatment of patients in critical situations. As earlier stated, AS plasma is universally accepted by everyone, no matter their blood type. Plasma is extracted via a machine that divides plasma from other blood elements, then smoothly and freely transports back your red blood cells and platelets to you.
Who can donate plasma?
If you want to donate plasma, you have to be 18 years of age and weigh no less than 50 kg or 110 pounds. You have to undergo and satisfy two medical tests, a medical history assessment and an examination for infectious viruses before you are allowed to donate plasma for blood therapies. Plasma donation is conducted in health facilities.
Who it assists:
AB plasma is highly valuable in health emergencies and life-threatening situations to reduce bleeding.
Time required:
An estimated 75 minutes.
Suitable blood types:
AB +, AB –
How often can I donate blood plasma?
Once every 28 days, no more than 13 times a year.
55% of your blood comprises plasma. It plays an important role in the body, which includes expelling waste products. Plasma is made up of 92% water. With this water, it occupies the blood vessels, which helps in the transportation of blood and other essential nutrients in the circulatory system.
The rest of the 8% of plasma is made up of other important materials like:
- proteins
- immunoglobulins
- electrolytes
When blood is broken down into its main components, such as plasma and red blood cells, plasma has an appearance that resembles a yellow fluid. A major importance of plasma is to transport hormones, proteins and nutrients around the different body parts that require them. It also carries waste products from cells and helps in the elimination of waste from the body. Blood plasma also transports the different elements of blood via your circulatory organs.
Why you shouldn’t donate plasma
- Dehydration
- drowsiness fainting, and feeling lightheaded
- Tiredness
- Bruising and pain
- Citrate reaction
- Arterial puncture
Has anyone died from donating plasma?
While plasma donation generally seems safe, there have been cases of deaths over the years
Long-term side effects of donating plasma regularly
There is a possibility of low immunoglobulin levels since it takes a while for the levels to get back to normal. Those who donate often and over time might be susceptible to anemia resulting from reductions in red cells during donation
Next-day side effects of donating plasma
For most individuals, donating plasma doesn’t result in any side effects, but certain donors may feel fatigue, bruising, bleeding, or dehydration. Furthermore, you might become faint or lightheaded. Although not common, fainting can also take place.
What do they test for when you donate plasma?
All donors have to be tested for HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C at every donation via nucleic acid amplification testing (NAT), a cutting-edge technique that checks for the DNA particles of the virus that causes these illnesses. In addition, each plasma donation undergoes testing for antibodies that the body yields when exposed to a virus.
Plasma donation weight chart
|
||||||||||||||||||
Why Do They Check Your Elbows When Donating Plasma? | Summary
1. Assessing Vein Health
The main reason for checking your elbows is to assess the condition of your veins. Plasma donation requires access to a strong, healthy vein that can sustain a steady blood flow throughout the donation process.
- The preferred vein for plasma donation is the median cubital vein, which is located in the bend of your elbow. This vein is large, stable, and provides an optimal flow rate for safe and efficient plasma extraction.
- If the vein appears too small, weak, or difficult to locate, the medical staff may advise against donation to prevent complications such as collapsed veins or difficulty returning blood components to your body.
2. Identifying Signs of Frequent Donations or Damage
For individuals who donate plasma regularly, repeated needle insertions can cause scarring or damage to the veins. Checking the elbows helps medical staff identify:
- Scar tissue or vein hardening from frequent donations, which may make it difficult to insert the needle properly.
- Bruising, swelling, or irritation, which could indicate that the vein needs time to heal before another donation.
- Phlebitis (vein inflammation) or other signs of poor vein health that might disqualify someone from donating temporarily or permanently.
3. Screening for Track Marks or Drug Use
Plasma donation centers have strict safety guidelines to protect both donors and plasma recipients. One aspect of this is screening for signs of intravenous (IV) drug use. Track marks—visible scars or puncture wounds along the veins—can indicate a history of drug use, which may pose risks such as:
- Bloodborne infections (HIV, hepatitis B, hepatitis C)
- Compromised vein integrity, making it unsafe to draw blood or return it to the donor
- Increased risk of contamination in the plasma supply
If visible signs of IV drug use are detected, the donor may be disqualified from donating plasma permanently or temporarily.
4. Checking for Signs of Skin Conditions or Infections
Since plasma donation involves inserting a needle directly into the vein, it’s essential to ensure that the surrounding skin is clean and free from infections. The elbow crease is checked for:
- Rashes, sores, or wounds that could increase the risk of infection during the donation process
- Signs of bacterial or fungal infections, which might lead to contamination of the donation site
- Recent tattoos or piercings, as they can introduce bacteria into the bloodstream and pose infection risks
5. Ensuring Overall Donor Safety
Plasma donation is generally a safe process, but it does put some temporary stress on the donor’s circulatory system. By examining the elbows, medical staff can determine whether the donor’s veins are healthy enough to handle the procedure. This helps prevent issues like:
- Excessive bleeding or bruising at the needle insertion site
- Difficulty in returning blood components, which can cause dizziness, fainting, or discomfort
- Vein collapse, which can make future donations more difficult and painful
What Happens If Your Elbows Don’t Pass the Check?
If the staff finds that your veins are not suitable for donation, they may advise you to:
- Stay hydrated and try again on another day (hydration helps improve vein visibility and elasticity).
- Take a break from donating if your veins show signs of stress or damage.
- Explore alternative ways to contribute, such as whole blood donation, which may require less vein durability.
In some cases, if your veins are consistently deemed unsuitable, you may be permanently deferred from plasma donation.
Tips for Keeping Your Veins Healthy for Plasma Donation
If you are a regular plasma donor or planning to start donating, here are some tips to keep your veins in good shape:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water before and after your donation to keep your veins plump and visible.
- Eat a healthy diet: Consuming iron-rich foods (such as leafy greens, lean meats, and beans) helps maintain strong blood vessels.
- Exercise regularly: Activities like weightlifting, yoga, and cardio help improve circulation and vein health.
- Avoid excessive caffeine and alcohol: These can dehydrate you, making your veins harder to access.
- Rotate donation arms: If possible, alternate arms to prevent excessive wear on one vein.
- Take breaks if needed: If you notice bruising or discomfort, allow time for healing before your next donation.
Conclusion
Checking your elbows before plasma donation is a simple but essential step to ensure both your safety and the quality of the plasma collected. By examining vein health, screening for infections, and identifying any signs of drug use or skin conditions, donation centers can maintain high safety standards for donors and recipients alike.
If you’re planning to donate plasma, taking care of your veins and overall health will help ensure a smooth and successful experience. Your contribution can make a significant difference in the lives of patients who rely on plasma-based treatments!
We hope you found this article helpful. Do well to check below for other related articles.
Recommended Read:
- What is Telehealth Urgent Care? (All you need to know)
- How to Get Medication Aide Certification (2025 Guide)
- What is Emergency Dental Care? (Comprehensive Guide 2025)
- Best schools to become a neurosurgeon
